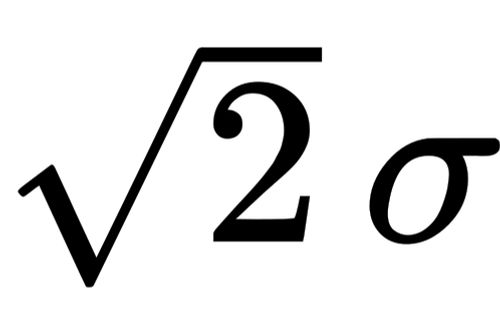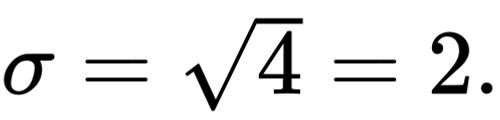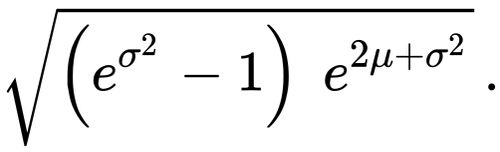Statistics - Calculating Mean given standard deviation and percentage. - Mathematics Stack Exchange
[Q] What is standard deviation exactly?
Why does the standard deviation formula square?
[Q][D] Why are the central limit theorem and standard error formula so similar?
Videos
dispersion of the values of a random variable around its expected value
Let the weight of the chickens be $X$. Then $X \sim N(\mu,\sigma^2)$ where $\sigma = 4.2$ is the standard deviation of the weights and $\mu$ is the mean of the weights. Then, the statement you're given is $P(X < 20) = 0.04$.
Now, rewrite $P(X<20) = P(X-\mu < 20-\mu) = P( \frac{X-\mu}{\sigma} < \frac{20-\mu}{\sigma}) = P(Z < \frac{20-\mu}{\sigma})$ where $Z \sim N(0,1)$. Then, look up $c$ in a standard normal table such that $P(Z<c) = 0.04$ and then note $\frac{20-\mu}{\sigma} = c$. Solve for $\mu$, and you are done.
You have to use the fact that the weights are normally distributed.
You're given the standard deviation, and a value for the left 4% of the distribution.
You can calculate (or look up) how many standard deviations away from the mean you are at 4%.
Given this, you multiply the number of standard deviations from the mean by the standard deviation (in lbs) to see how many lbs away from the mean you are.
You know one end (20 lbs) and you can now find the other end, which is the mean.