chemical compound
Factsheet
Names IUPAC name
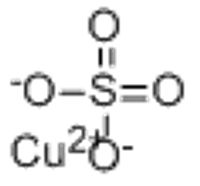
Copper(II) sulfate
Copper(II) sulfate
Identifiers
CAS Number 7758-98-7 (anhydrous) Y
7758-99-8 (pentahydrate) Y
16448-28-5 (trihydrate) N
19086-18-1 (heptahydrate) N
7758-99-8 (pentahydrate) Y
16448-28-5 (trihydrate) N
19086-18-1 (heptahydrate) N
Names IUPAC name
Copper(II) sulfate
Copper(II) sulfate
Identifiers
CAS Number 7758-98-7 (anhydrous) Y
7758-99-8 (pentahydrate) Y
16448-28-5 (trihydrate) N
19086-18-1 (heptahydrate) N
7758-99-8 (pentahydrate) Y
16448-28-5 (trihydrate) N
19086-18-1 (heptahydrate) N
Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Copper(II)_sulfate
Copper(II) sulfate - Wikipedia
December 6, 2025 - Copper(II) sulfate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula · CuSO4. It forms hydrates · CuSO4·nH2O, where n can range from 1 to 7. The pentahydrate (n = 5), a bright blue crystal, is the most commonly encountered hydrate of copper(II) sulfate, while its anhydrous form is white.
Videos
05:14
Solubility of copper sulfate and copper carbonate - YouTube
01:57
Is CuSO4 Soluble or Insoluble in Water? - YouTube
02:27
Equation for CuSO4 + H2O | Copper (II) sulfate + Water - YouTube
05:07
[Chemistry] The solubility of copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate ...
13:25
Preparation of Copper Sulfate Crystals - YouTube
Solubility of copper(II) sulfate problem
That is not what I get -- though close. How about, show what you did -- clearly, and we can look. More on reddit.com
Solubility of copper sulfate complex in acetic acid
Both plain copper sulfate and your copper ammonia sulfate complex are a lot more soluble in water than copper acetate. So you are quite right that your precipitate is copper acetate. If you add acetic acid slowly enough to the copper ammonia sulfate solution, you should see a colour change from deep purple to blue before the precipitate forms. This is because to begin with, some of the acetic acid will react with the ammonia, protonating it to form NH*4*+ ions, which cannot bind to the copper. As more acetic acid is added, the copper precipitates as Cu(OAc)2 solid. Excess acetic acid will drag this back into solution by forming the Cu(OAc)*3*- complex ion, which looks like this . More on reddit.com
Why is the answer D and not C? Copper(II) sulfate is soluble in water so won't be found in a powder, no?
Copper(II) sulfate must have been present in the powder for it to dissolve. The question is asking what was in the powder before water was added. More on reddit.com
Why do Hydrated Copper (II) Sulfate crystals not dissolve from the water or crystallisation?
In rough terms, because there is not enough water for that. The hydrate is a pentahydrate salt IIRC. It is just the right amount of water to exist in the solid phase, lodged in between the ions. More on reddit.com
Sciencemadness Wiki
sciencemadness.org › smwiki › index.php › Copper(II)_sulfate
Copper(II) sulfate - Sciencemadness Wiki
August 26, 2023 - Copper(II) sulfate is a blue crystalline solid as the pentahydrate, as it is most commonly seen, and the anhydrous form is a white to light gray powder. It has a solubility of 31.6 g/100 mL at 0˚C and 203.3 g/100 mL at 100˚C.
Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Copper(I)_sulfate
Copper(I) sulfate - Wikipedia
July 20, 2025 - The material is stable in dry air at room temperature but decomposes rapidly in presence of moisture or upon heating. It decomposes into copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate upon contact with water.
Oregon State University
npic.orst.edu › factsheets › archive › cuso4tech.html
Copper Sulfate Technical Fact Sheet
Citrus root stock seedlings (Swingle citrumelo) were then transplanted into the pots and allowed to grow for 330 days. In two of three soils, citrus seedlings had reduced leaf, stem, and root dry weights at greater copper application rates. Readily soluble copper increased with decreasing soil ...
ILO
chemicalsafety.ilo.org › dyn › icsc › showcard.display
ICSC 1416 - COPPER(II) SULFATE, PENTAHYDRATE
According to UN GHS Criteria · Transportation UN Classification
Sciencemadness
sciencemadness.org › talk › viewthread.php
Sciencemadness Discussion Board - Solubility of copper sulphate compared to its pentahydrate - Powered by XMB 1.9.11
March 5, 2023 - FAQ Forum Library Wiki Member publications Los Alamos Technical Reports
OIV
oiv.int › standards › international-oenological-codex › part-i-monographs › monographs › copper-sulfate,-pentahydrate
Copper sulfate, pentahydrate | OIV
An aqueous solution with ammonium hydroxide (R) produces a dark blue copper tetramine compound. A solution acidified with hydrochloric acid and a barium chloride solution (R) produces a white barium sulfate precipitate.
Reddit
reddit.com › r/chemhelp › solubility of copper(ii) sulfate problem
r/chemhelp on Reddit: Solubility of copper(II) sulfate problem
September 12, 2023 -
I am trying to solve a problem and I think I did but don't have solutions to check it. Here is the problem:
The solubility of anhydrous copper(II) sulfate at 100 C is 4.72 mol/kg. How much copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate can be obtained from 306 g of such a saturated solution?
I got that 206 g of copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate can be obtained. Could someone check, please?
ScienceDirect
sciencedirect.com › topics › biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology › copper-ii-sulfate
Copper(II) Sulfate - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
The melting point is 1083°C with a boiling point of 2595°C. Copper has two stable isotopes, 63Cu and 65Cu, with natural abundances of 69.2 and 30.8%, respectively (Georgopoulos et al., 2001). The water solubility of copper (II) sulfate is 143 g/L at 0°C, whereas cuprous(I) oxide and copper ...
Oregon State University
npic.orst.edu › factsheets › cuso4gen.html
Copper Sulfate Fact Sheet
Copper sulfate is highly soluble in water and it can bind to sediments. Copper is regulated by plants because it is an essential mineral.