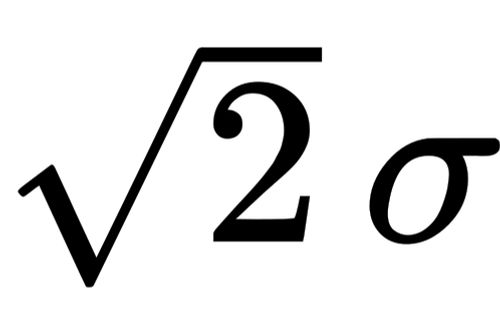Calculator.net
calculator.net › home › math › standard deviation calculator
Standard Deviation Calculator
The equation provided below is the "corrected sample standard deviation." It is a corrected version of the equation obtained from modifying the population standard deviation equation by using the sample size as the size of the population, which removes some of the bias in the equation.
Calculating population standard deviation - Statalist
Stata simply refers to "standard deviation", without really mentioning anything about the distinction between sample and population. I can see that I could achieve my goal with some manually input formula, but I struggle to believe that Stata doesn't have a command for doing this. More on statalist.org
Calculating Standard Deviation
Hi, u/Salt_Gap_1592 ! This is an automated reminder: What have you tried so far? (See Rule #2; to add an image, you may upload it to an external image-sharing site like Imgur and include the link in your post.) Please don't delete your post. (See Rule #7) We, the moderators of r/MathHelp , appreciate that your question contributes to the MathHelp archived questions that will help others searching for similar answers in the future. Thank you for obeying these instructions. I am a bot, and this action was performed automatically. Please contact the moderators of this subreddit if you have any questions or concerns. More on reddit.com
[Gen Chem 1: Standard Deviation] Why is my calculated standard deviation different from Excel's?
You calculated the standard deviation of a population. Excel's function calculates the standard deviation of a sample. More on reddit.com
[Q][D] Why are the central limit theorem and standard error formula so similar?
The CLT is about the sampling distribution of a statistic. The standard error is about the variance (or standard deviation) of a statistic. The similarity is mostly in the context of what I'd characterize as "intro stats" level, where the focus is almost entirely on means of some sort. In that context, "the" CLT (there are variants of it) says that if we're talking about a mean, then the sampling distribution will get closer and closer to a Normal distribution as the sample size increases. That Normal distribution will have a mean and a variance (or standard deviation). The standard deviation of that distribution is the standard error of the sample mean. But the sample mean will have a standard error regardless of whether the sampling distribution of the sample mean is Normal or not. And other statistics than the sample mean have a version of the CLT (with a different standard error). The difference between s and σ is the difference between talking about a sample and talking about the population. When using σ we're talking about the standard deviation of the population, of which s is an estimate. Similarly, σ/√n is the standard error of the sample mean of the population (when taking a sample of size n), but s/√n is an estimate of that value. More on reddit.com
Videos
02:06
How To Calculate Sample Standard Deviation (Step By Step) - YouTube
Standard Deviation and Variance of a Population │Statistics - ...
07:14
How To Calculate The Standard Deviation - YouTube
05:39
Find Standard Deviation by Hand (Population OR Sample) - YouTube
How to Find Sample Standard Deviation in Minutes! - YouTube
dispersion of the values of a random variable around its expected value
Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Standard_deviation
Standard deviation - Wikipedia
6 days ago - As explained above, while s2 is an unbiased estimator for the population variance, s is still a biased estimator for the population standard deviation, though markedly less biased than the uncorrected sample standard deviation. This estimator is commonly used and generally known simply as the "sample standard deviation". The bias may still be large for small samples (N less than 10). As sample size increases, the amount of bias decreases. We obtain more information and the difference between ... For unbiased estimation of standard deviation, there is no formula that works across all distributions, unlike for mean and variance.
Laerd Statistics
statistics.laerd.com › statistical-guides › measures-of-spread-standard-deviation.php
Standard Deviation | How and when to use the Sample and Population Standard Deviation - A measure of spread | Laerd Statistics
Therefore, you would normally calculate the population standard deviation if: (1) you have the entire population or (2) you have a sample of a larger population, but you are only interested in this sample and do not wish to generalize your findings to the population.
Standard Deviation Calculator
standarddeviationcalculator.io
Standard Deviation Calculator - Sample/Population
Step 2: Calculate (xi - x̄) by ... + 2.78 + 40 + 5.43 + 113.85 + 21.80 ... Step 4: Divide ∑(xi - x̅)2 with (N-1). ... Step 5: Take the square root of ∑(xi - x̅)2/(N-1) to get the standard deviation....
Microsoft Support
support.microsoft.com › en-us › office › stdev-p-function-6e917c05-31a0-496f-ade7-4f4e7462f285
STDEV.P function - Microsoft Support
Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population given as arguments (ignores logical values and text).
DataCamp
datacamp.com › tutorial › sample-standard-deviation
Sample Standard Deviation: The Key Ideas | DataCamp
September 26, 2024 - Sample standard deviation formula. Image by Author. ... Note that when calculating the sample standard deviation, we use n-1 in the denominator to correct the sample bias. This is known as Bessel’s correction. If we were interested in the population standard deviation, we would use n in the ...
Microsoft Support
support.microsoft.com › en-us › office › stdev-function-51fecaaa-231e-4bbb-9230-33650a72c9b0
STDEV function - Microsoft Support
STDEV assumes that its arguments are a sample of the population. If your data represents the entire population, then compute the standard deviation using STDEVP.
YouTube
youtube.com › learn2stats
How to Calculate Population Standard Deviation (Step-by-Step) - YouTube
This video, in statistics, shows the tutorial of how to calculate the population standard deviation. First, it goes over the notation differences between the...
Published December 31, 2020 Views 88K
Simple Book Publishing
open.maricopa.edu › haasstatistics › chapter › 4-5-calculating-standard-deviation
4.6 – Calculating Standard Deviation – Introduction to Statistics and Statistical Thinking
August 8, 2022 - [latex]\text{Population Standard Deviation}=\sigma=\sqrt{\sigma^2}[/latex] [latex]\text{Sample Standard Deviation}=s=\sqrt{s^2}[/latex] Let's continue using the same set of scores with which we have been working: [latex]\text{Sum of Squares (Computational Formula)}=SS=\Sigma X^2-\frac{(\Sigma X)^2}{N}[/latex]
Hunter College
hunter.cuny.edu › dolciani › pdf_files › brushup-materials › calculating-variance-and-standard-deviation.pdf pdf
Calculating Variance and Standard Deviation
Skip to content. | Skip to navigation · About Mary P. Dolciani DMLC Mission
Cuemath
cuemath.com › data › standard-deviation
Standard Deviation - Formula | How to Calculate Standard Deviation?
To adjust this, the denominator of the sample standard deviation is corrected to be n-1 instead of just n. This is known as Bessel's correction. There are two types of data sets: populations and samples. A population is an entire group that we are interested in studying, while a sample is a smaller group of individuals that is taken from the population. The formulas to calculate the standard deviations of population and sample differ a little.
Statalist
statalist.org › forums › forum › general-stata-discussion › general › 1381078-calculating-population-standard-deviation
Calculating population standard deviation - Statalist
March 30, 2017 - There are no built-in functions or -egen- functions that calculate the population standard deviation. In most situations, the sample standard deviation is what is wanted. And it is not hard to transform the sample estimate into the population standard deviation: just multiply by sqrt((N-1)/N).