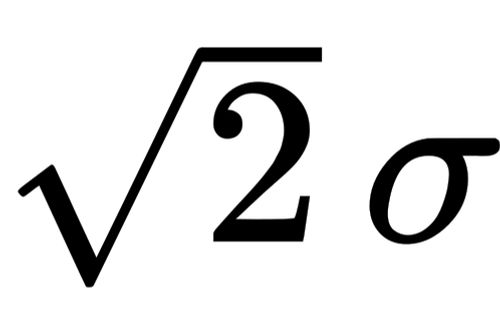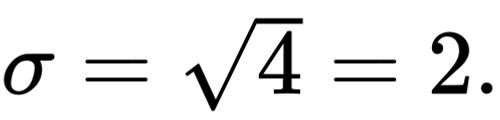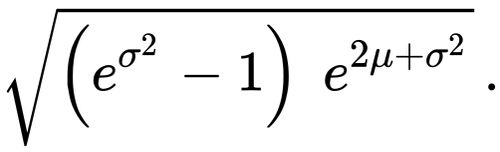statistics - Relationships between mean and standard deviation when one variable is linear function of another - Mathematics Stack Exchange
[Q] Is standard deviation the average difference of values to the mean?
What can be determined on the relationship between the mean, standard deviation, and the shape of a normal distribution?
What is the relation between the mean and SD to consider the the data is convergent?
Videos
dispersion of the values of a random variable around its expected value
The mean of
= mean of
This is not true.
The way you should approach this problem is to use the formulas for mean and standard deviation directly: \begin{align*} \text{Mean}(y_1, y_2, \ldots, y_n) &= \frac{y_1 + y_2 + \cdots + y_n}{n} \\ &= \frac{(ax_1 + b) + (ax_2 + b) + \cdots + (ax_n + b)}{n} \\ &= \frac{a(x_1 + x_2 + \cdots + x_n) + nb}{n} \\ &= a \cdot \text{Mean}(x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n) + b \\ \end{align*}
See if you can do a similar algebraic manipulation for standard deviation.
Since , then
Use the same way with SD
I distinctly remember my intro professor describing it as such, but when I asked my upper division professor, he said that wasn't true because you square the differences.
But standard deviation requires you to take the square root of the differences at the end of the calculation, so doesn't it make it back to average again? Maybe the slight difference is from n-1 on the formula...