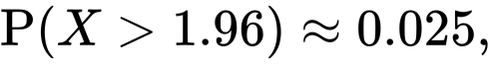Pindling
pindling.org › Math › Learning › Statistics › z_scores_table.htm
Appendix - z-score percentile for normal distribution
Appendix - z-score percentile for normal distribution
Videos
Find Percentile with Mean and Standard Deviation (Normal Curves) ...
03:42
Finding Normal Percentiles Using a Z Score Table - YouTube
07:26
How To Find The Z Score Given The Confidence Level of a Normal ...
01:49
Finding the z score associated with the top 5th percentile of the ...
15:23
Finding Percentiles for a Normal Distribution - YouTube
How to compute for percentile using z-score - YouTube
What is a Z-score?
A Z-score (or standard score) measures how many standard deviations a data point is from the mean. It's calculated as: Z = (X - μ) / σ, where X is the value, μ is the mean, and σ is the standard deviation.
z-table.com
z-table.com › z-scores-to-percentiles-chart.html
Z Scores to Percentiles Chart - Z SCORE TABLE
How do you use a Z-score table?
To use a Z-score table: 1) Calculate your Z-score, 2) Find the row matching the first two digits, 3) Find the column for the second decimal place, 4) The intersection gives you the probability or area under the normal curve.
z-table.com
z-table.com › z-scores-to-percentiles-chart.html
Z Scores to Percentiles Chart - Z SCORE TABLE
What is a confidence interval?
A confidence interval is a range of values that likely contains the true population parameter. For example, a 95% confidence interval means we're 95% confident the true value falls within that range. Z-scores help calculate these intervals.
z-table.com
z-table.com › z-scores-to-percentiles-chart.html
Z Scores to Percentiles Chart - Z SCORE TABLE
CDC
cdc.gov › growthcharts › extended-bmi-data-files.htm
Growth Charts - Data file for the CDC Extended BMI-for-Age Growth Charts
BMI percentiles and z-scores up to the 95th percentile (z-score 1.645) are the same as those in the 2000 CDC BMI-for-age growth charts and the L,M,S parameters, selected percentiles (3rd, 5th, 10th, 25th, 50th, 75th, 85th, 90th, 95th), and z-scores (-2, -1.5, -.5, 0, .5, 1, 1.5) are identical ...
number useful in statistics for analyzing a normal curve
Wikipedia
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › 97.5th_percentile_point
97.5th percentile point - Wikipedia
May 4, 2025 - From the probability density function ... {2\pi }}}\int _{-z_{.975}}^{z_{.975}}e^{-x^{2}/2}\,\mathrm {d} x=0.95.} Its square, about 3.84146, is the 95th percentile ......
NYU Stern
pages.stern.nyu.edu › ~churvich › MBA › Handouts › 8-Normal.pdf pdf
8. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
P(−3 ≤Z ≤3) = 2(0.4987) = 0.9974. Note: This shows that the empirical rule holds for standard · normal distributions. We still need to prove it for general normal ... So the 95th percentile is 1.645.
Z Score Table
z-table.com › z-scores-to-percentiles-chart.html
Z Scores to Percentiles Chart - Z SCORE TABLE
Using the Percentiles to Z Score Chart is relatively simple. First, find the percentile in the chart that corresponds to the data point you want to analyze. Then, locate the Z Score value in the same row as the percentile. This Z Score value indicates the number of standard deviations the data point is away from the mean.
Khan Academy
khanacademy.org › math › ap-statistics › density-curves-normal-distribution-ap › normal-distributions-calculations › v › finding-z-score-for-a-percentile
Finding z-score for a percentile (video)
We cannot provide a description for this page right now
Boston University
sphweb.bumc.bu.edu › otlt › mph-modules › bs › bs704_probability › bs704_probability10.html
Computing Percentiles
In some instances it may be of interest to compute other percentiles, for example the 5th or 95th. The formula below is used to compute percentiles of a normal distribution. where μ is the mean and σ is the standard deviation of the variable X, and Z is the value from the standard normal ...
Brainly
brainly.com › mathematics › high school › find the z-values corresponding to the following percentiles of the standard normal distribution:
(a) the 75th percentile
(b) the 90th percentile
(c) the 95th percentile
(d) the 99th percentile
[FREE] Find the z-values corresponding to the following percentiles of the standard normal distribution: (a) The - brainly.com
... Introduction to Statistics in the Psychological Sciences - Linda R. Cote · Upload your school material for a more relevant answer · The z-values for the specified percentiles are approximately: 75th = 0.674, 90th = 1.28, 95th = 1.645, and ...
Chegg
chegg.com › math › statistics and probability › statistics and probability questions and answers › find the z score for the 95th percentile. z = [____] round to 2
d.p.
Solved Find the Z score for the 95th percentile. Z = [____] | Chegg.com
September 1, 2021 - Answer to Find the Z score for the 95th percentile. Z = [____]
Brainly
brainly.com › mathematics › high school › find the z-score that marks the 95th percentile (denoted as p95). then find the z-score that delineates the lower 95% from the upper 5% of all the z-scores. enter your answer to 2 or 3 decimal places.
[FREE] Find the z-score that marks the 95th percentile (denoted as P95). Then find the z-score that delineates the - brainly.com
The z-score that marks the 95th percentile is approximately 1.645.
Chegg
chegg.com › math › statistics and probability › statistics and probability questions and answers › how to find the 95th percentile of the standard normal distribution? answer: area to the left of the z-score is 0.95 and it is positive. go to the table and find the corresponding z-score. the z score will be positive....how do you know this?
Solved How to find the 95th percentile of the standard | Chegg.com
June 15, 2022 - How to find the 95th percentile of the standard normal distribution? Answer: Area to the left of the Z-score is 0.95 and it is positive. Go to the table and find the corresponding Z-score.
My Math Tables
mymathtables.com › statistic › z-score-percentile-normal-distribution.html
Z Score Percentile Distribution Table
Z Score Calculator Z Score to Percentile Calculator · H1: parameter < value · Notice the inequality points to the left · Decision Rule: Reject H0 if t.s. < c.v. H1: parameter > value · Notice the inequality points to the right · Decision Rule: Reject H0 if t.s.