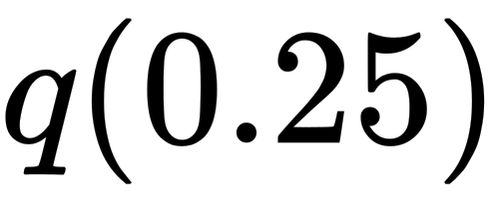Videos
How do I find quartiles in Excel?
How do I find quartiles in R?
How do I find the quartiles of a probability distribution?
the three points that divide the data set into four equal groups in descriptive statistics
I have a problem with the calculation of a quartile. I need the first quartile of a simple enumeration. But I need the exact value not the simplified form. With Wolfram Alpha I get 28, with Excel 29. And for manual interpolation my math skills are not sufficient. Which of the two can I trust?
The data set is:
-
26
-
30
-
46
-
99
With Excel: =QUARTILE.INKL(A1:A4;1)=29
With Wolfram Alpha: 28
I would be very grateful if someone could help me
The first quartile should have at least $\frac14$ of the data points at or below it and at least $\frac34$ of the data points at or above it. In the case where the number of data points is divisible by $4$, there can be a gap between the greatest value in the first $\frac14$ of the data points and the least value in the last $\frac34$ of the data points, and then there is a convention to put the first quartile midway between those two points.
For the first quartile, then, if there are $n$ data points then you can compute $k = \frac n4$. If $k$ is an integer, you count off $k$ values starting with the smallest, and put $Q_1$ midway between the $k$th value and the $(k + 1)$th value. If $k$ is not an integer, you count off $\lfloor k \rfloor$ data points and $Q_1$ is the next data point.
The third quartile works similarly, but with $k = \frac 34 n$ instead of $\frac n4$.
It's important to remember that $n$ in these formulas is not one of the data values, and you do not add the result of $\frac n4$ to any data value; you use $\frac n4$ to count data values.
It's not clear where you got the formulas $\frac14(n+1)$ or $\frac34(n+1)$. Perhaps they were intended to work with a data set labeled $y_0, y_1, y_2, \ldots, y_n$, which actually has $n+1$ data points because its first data point is $y_0$.
Many different formulas for quantiles (including quartiles) are in common use. That is because quantiles are used with many different distributions and for many different purposes.
In particular, major statistical software packages disagree on which methods to implement as their default: (a) SAS, (b) Minitab and SPSS, and (c) R (and its parent S) use three different methods. Furthermore, these methods differ from methods found in reputable elementary texts, including the method mentioned in the Answer by @David K. (Adding to the confusion: Tukey's 'fourths', sometimes used in making boxplots and often considered essentially the same as quartiles, use yet other criteria.)
Generally speaking the differences among these methods become negligible for large sample sizes. However, there can be marked differences for small samples. Fortunately, it is for large samples that quantiles make the most sense. (Roughly, quartiles are intended to divide a sample into four 'chunks' of equal size: how do you do that with a sample of size 10?)
Here is a demo using R software, which allows use of the
parameter type to change its default method. By default
the R function quantile gives min, lower quartile, median,
upper quartile, max. (Parameters can be used to specify other
quantiles as desired.)
x = round(rnorm(10, 100, 15), 1) # 10 obs. from NORM(100, 15) rounded to 1 place.
sort(x)
## 73.7 81.5 83.5 96.3 104.6 106.2 113.8 114.2 116.4 117.4
quantile(x) # R default
## 0% 25% 50% 75% 100%
## 73.7 86.7 105.4 114.1 117.4
quantile(x, type=3) # as in SAS
## 0% 25% 50% 75% 100%
## 73.7 81.5 104.6 114.2 117.4
quantile(x, type=6) # as in Minitab & SPSS
## 0% 25% 50% 75% 100%
## 73.70 83.00 105.40 114.75 117.40
fivenum(x) # Tukey's 'fourths' (actual sample values, not strictly quartiles)
## 73.7 83.5 105.4 114.2 117.4
x = round(rnorm(1000, 100, 15), 1) # n = 1000; all about the same
# 111.4 repeated
quantile(x)
## 0% 25% 50% 75% 100%
## 57.60 89.45 99.85 111.40 153.70
quantile(x, type=3)
## 0% 25% 50% 75% 100%
## 57.6 89.3 99.8 111.4 153.7
quantile(x, type=6)
## 0% 25% 50% 75% 100%
## 57.60 89.35 99.85 111.40 153.70
fivenum(x)
## 57.60 89.40 99.85 111.40 153.70
If you have access to R (available free from www.r-project.org), you can
type ? quantile and read some details of nine different
types of quantiles--about halfway down the page.